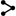In today’s fiercely competitive business landscape, understanding the components that contribute to your company’s success is crucial. Value Chain Analysis is a powerful tool that allows businesses to dissect their operations, identify areas of value creation, and gain a competitive advantage. In this blog, we will explore what Value Chain Analysis is, how to use it, and its role in establishing a competitive edge.
What Is Value Chain Analysis?
Value Chain Analysis is a strategic management tool introduced by Michael Porter in his book “Competitive Advantage” in 1985. It provides a systematic approach to analyzing a company’s activities and operations to understand how value is created throughout its production and delivery process. The primary goal of this analysis is to identify opportunities for optimization, cost reduction, and differentiation to increase a company’s overall efficiency and profitability.
Value Chain Components:
The value chain is a sequence of activities that a company performs to deliver its products or services to customers. It comprises two types of activities:
1. Primary Activities:
These are directly involved in the creation and delivery of the product or service. The primary activities include:
- Inbound Logistics: Receiving, storing, and distributing raw materials for production.
- Operations: The actual transformation process of raw materials into finished products.
- Outbound Logistics: Managing the storage, distribution, and delivery of the finished products to customers.
- Marketing and Sales: Activities to promote and sell the products to potential customers.
- Customer Service: Providing after-sales support and handling customer inquiries.
2. Support Activities:
These activities support the primary activities and play a vital role in optimizing the value chain. The support activities include:
- Procurement: Sourcing and acquiring the necessary raw materials and resources.
- Human Resources: Recruitment, training, and development of employees to enhance productivity.
- Technology Development: Research, development, and innovation to improve products and processes.
- Infrastructure: Management and support services, such as finance, legal, and administration.
How to Use Value Chain Analysis:
To perform a Value Chain Analysis, follow these steps:
1. Identify the Value Chain Activities:
List all the activities involved in creating and delivering your products or services. Categorize them into primary and support activities.
2. Assess Each Activity’s Value:
Analyze each activity to understand its contribution to the final product or service and its impact on costs.
3. Identify Cost Drivers:
Determine the factors that influence the costs associated with each activity, such as economies of scale, resource availability, or technology.
4. Analyze Linkages:
Examine the relationships between activities. Improvements in one area may lead to cost reductions or increased effectiveness in others.
5. Competitive Benchmarking:
Compare your value chain against competitors to identify areas where you may be lagging or outperforming.
What Is Competitive Advantage?
Competitive advantage refers to the unique attributes or resources that allow a company to outperform its rivals and achieve a superior market position. Value Chain Analysis plays a critical role in creating competitive advantage by helping businesses:
1. Cost Advantage:
Identify cost-efficient activities and streamline processes to lower production costs while maintaining quality.
2. Differentiation:
Recognize areas where products or services can be differentiated to meet customer needs better.
3. Focus Strategy:
Concentrate efforts on specific activities or market segments where the company can excel.
Value Chain Analysis is a powerful tool that enables businesses to identify critical activities, optimize operations, and gain a competitive edge. By understanding their value chain and using the insights gained, companies can improve efficiency, reduce costs, and deliver products or services that stand out in the market. By continuously reassessing their value chain, businesses can adapt to changing market dynamics and maintain a sustainable competitive advantage in the long term.